If you are thinking about start mining or already and decided to go for it, you will asking which is better for mining SSD or HDD ?
If you think that SSD will make mining faster, it is not. Mining will not be accelerated. It will reduce energy usage by a tiny amount. It will also reduce startup times and the time it takes for GPU OC/Power settings to load.
In this article you will learn:
SSD vs HDD for Mining Hardware
The first blockchain gave birth to the cryptocurrency industry. Mining was not previously associated with computers. With the expansion of this sector, so does the use of unconventional gear and innovation. Mining's potential is demonstrated by SSDs. The imitations of traditional HDDs to grow in comparison become apparent.
AN INTRODUCTION TO BLOCKCHAIN MINING
The purpose of specialised mining rigs as an essential feature of the original blockchain is transaction processing by miners. Mining equipment is now used for both proof of work (POW) and proof of stake (POS – validating transactions). This demonstrates the symbiotic relationship between miners and the bitcoin market. Here's a real-world question-and-answer session regarding the advantages and disadvantages of various mining gear.
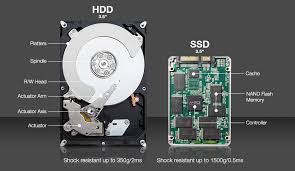
Solid state drives (SSD) and hard disc drives (HDD) are the two types of devices utilised in mining (HDD). They're used in similar ways by miners. SSDs have a number of advantages, the most important of which is the ability to access data significantly faster than HDDs. SSDs are currently not completely superior to HDDs.Learn more about the drives that are used to mine blockchains.
SATA
Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA, or Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) is a storage device interface. It is linked to the host bus. Cooling is aided by the smaller cables it employs. Speeds of 150 MBps and more are common. SATA cables can be used with both SSDs and HDDs. It's important to note that a SATA hard drive refers to a hard disc drive (HDD). Here's where you can learn more about SATA.
Over the course of a decade, SATA hard drives have been found to withstand intensive use. If one wants the hard disc to last thus long, it's probably not a good idea to run them around the clock. In terms of speed, HDDs can't match SSDs' ability to fully utilise SATA capabilities.
HDD
A hard disc drive (HDD) has a transfer rate of 100-120 MBps. In comparison to an SSD, this is regarded to be extremely slow. A Windows-based HDD is not recommended for mining. For an HDD, just installing Windows would take a long time, but not for an SSD.
SSD
Solid-state drives (SSDs) are more durable than hard disc drives (HDDs). This is true even if the machine is running 24 hours a day, seven days a week. They may operate at high levels of utilisation for almost a decade. The biggest reason for having an SSD, though, is that the reboots appear to be much faster than HDD reboots.
The SATA III cables have a speed limit of 550 MBps. This limit is readily exceeded with SSD. It can even occupy the PCI Express (PCIe) bus's 3500 MBps bandwidth. The PCIe differs from the others in that it employs the NVM Express interface.
SPEED DISTINCTIONS
The stated speeds vary depending on the version and other factors. It's simple to switch speeds. The connection speed is not the same as the driving speed. A SATA III connection, for example, can achieve 6 Gbps.
It's very simple to mix up the units. It's important to remember that megabytes are the unit of measurement (not megabits). Megabits per second (MBps) and Megabytes per second (MBps) are not the same thing (mbps). A megabit is eight times larger than a megabyte. Units are a typical blunder.
RELIABILITY
Since 2010, SSDs have come a long way. There was a known problem with these drives dying frequently. The problems that hampered SSDs were exploited by HDD manufacturers. SSD adoption was limited as a result of this. SSDs, on the other hand, would quickly outperform HDDs in terms of reliability. SSDs have proven to be dependable in long-term, continuous use. Even so, it's a good idea to have a backup and/or RAID. One never knows when hardware will be damaged by an unforeseen event.
NEEDS AND NUANCES OF MINING
It's impossible to mine alone. It used to be possible to make money mining with an ordinary computer. Those were the days. To solo mine today, you'll need at least 1000 Mhps.
In today's economy, mining in a pool is considerably more feasible. Now, a total of 40 GB would suffice. An AMD or Nvidia driver can be used to accomplish this. In this configuration, one can mine in a pool using Windows and a miner. It is not essential to download the blockchain to a computer. Having a PC wallet isn't either.
RECOMMENDATIONS
When it comes to SSDs, speed isn't as important as it once was. This is due to the fact that modern models can utilise the SATA III connection to its full potential. At the time, there is no discernible speed difference between SSDs.
With that in mind, Samsung is a well-known name in the industry. Their products are among the best in the industry. The company constantly produces high-quality goods. Customers are reassured by their excellent customer service and warranty policy. All of this comes at a reasonable cost.
The 850 series from Samsung is one of the best SATA III SSDs on the market. Most recreational miners should be able to get by with the 850 Evo. The 850 Pro is a serious camera. Miners benefit from a better atmosphere and warranty as a result of the additional expense.
A 950 line from Samsung connects to a PCIe slot. This is the same connection that the GPU employs. The result is a speed increase of over 5 times. However, the speed boost isn't considerable in mining. This product may be useful to some miners who have high-end computers. It'll only cost you an extra $70. Samsung offers an Evo and Pro model, similar to the 850 range.
COST
Electricity costs are a common source of dissatisfaction among miners. SSDs are more expensive, but they use less power. Consumers can get more out of cheap SSDs than just a low price. Some people's time is inextricably linked to their earnings. As a result, selecting an SSD is a no-brainer. When you consider that SSD prices are continuing to decline, it's evident that SSDs are the better long-term investment.
The rate of change in this field is mind-boggling. The cryptocurrency and blockchain marketplaces, which are dominated by Ethereum and Bitcoin, are spurring innovation across industries. SSDs may become far more lucrative in the future.
What are storage miners?
Storage mining is a sort of cryptocurrency mining in which miners are rewarded for storing data on their own computers or devices. One of the fundamental concepts of storage mining is that miners must commit a particular amount of storage space in order to be eligible to join the blockchain network as a node.
Filecoin is one of the most well-known cryptocurrencies that relies on storage mining for its operations. In order to choose suitable nodes, the Filecoin blockchain relies on the storage capacity of its miners. These nodes then operate as transaction verifiers and miners for newly added blocks to the chain.
In the bitcoin sector, entrusting the node selection process to a storage-based consensus mechanism is a bit of an experiment. Proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus procedures are used by the majority of popular blockchains. Blockchains like Filecoin, on the other hand, use storage power as a criterion for node eligibility. Validators for nodes are chosen based on the amount of storage capacity they can provide to the network. Nodes or storage miners receive mining rewards in exchange. For successful block creation in Filecoin, storage miners win FIL tokens.
Users of the Filecoin blockchain and system benefit from the storage that miners contribute to the network. This is why the consensus method requires all approved notes to demonstrate that they have the necessary storage capacity and that they always keep an up-to-date copy of the entire system on their servers.
Storage miners, interestingly, have the option of dedicating cloud storage or hardware storage. This makes acquiring additional storage power and moving up the node rankings quite simple for storage miners.
Although storage-based consensus mechanisms are rarely used in the blockchain sector, Filecoin is proof that they can work. Furthermore, the very configurable criteria for the sort of storage power demanded by the network provide great freedom to storage miners. More established consensus mechanisms do not usually allow for this flexibility in node requirements.
What Is Proof of Capacity (PoC) for Cryptocurrencies?
Proof of capacity (PoC) is a consensus mechanism method used in blockchains that allows mining devices in the network to decide mining rights and validate transactions using their available hard drive space. This is in contrast to using the processing power of the mining device (as in the proof of work method) or the miner's cryptocurrency stake (as in the proof of stake algorithm).
Understanding Proof of Capacity
Proof of capacity is one of many alternatives to the problems of high energy consumption in proof of work (PoW) systems and coin hoarding in proof of stake (PoS) systems.
Proof of capacity allows mining devices on the blockchain network, commonly known as nodes, to mine available bitcoins using free space on their hard drives.
PoC works by storing a list of possible solutions on the mining device's hard drive even before the mining activity begins, rather than continuously changing the numbers in the block header and hashing for the solution value as in a PoW system.
The more alternative solution values a miner can keep on his hard drive, the more chances he has to match the required hash value from his list, resulting in a higher possibility of winning the mining prize.
To provide an illustration, if lottery prizes are determined by matching the most numbers on the winning ticket, a player with a broader range of potential answers will have a better chance of winning. Furthermore, the player is able to use the lottery ticket block numbers over and over again.
Burstcoin is a cryptocurrency that operates on the proof-of-capacity principle. Storj, Chia, and SpaceMint are among the coins that use it.
How PoC Works: Plotting and Mining
Plotting and mining are two steps in the proof-of-capacity protocol.
First, the hard drive is plotted: a list of all potential nonce values is constructed by hashing data, including a miner's account, over and over again. Each nonce is made up of 8192 hashes, numbered from 0 to 8191. All of the hashes are coupled into "scoops," which are groups of two neighbouring hashes. For example, hash 0 and 1 equals scoop 0, hash 2 and 3 equals hash 1, and so on.
The second phase is the actual mining, which entails calculating a scoop number by a miner. For example, if a miner starts mining and generates scoop number 38, the miner would then go to nonce 1's scoop number 38 and utilise the data from that scoop to calculate a deadline value.
For each nonce stored on the miner's hard drive, the process is repeated to calculate the deadline. The miner chooses the one with the shortest deadline after calculating all of the deadlines.
Before a miner is authorised to produce a new block, a deadline represents the amount of time in seconds that has passed since the last block was forged. The miner can fabricate a block and claim the block reward if no one else has done so inside this time frame.
For example, if miner X sets a minimum deadline of 36 seconds and no other miners can forge the block within that time, X will be guaranteed the opportunity to forge the next block and be rewarded.
Pros and Cons of Proof of Capacity
PoC has a number of advantages over PoW and PoS systems, as well as some significant drawbacks, including:
Pros
- Any normal hard drive, including those with Android-based systems, can be used by PoC.
- It is said to be up to 30 times more energy efficient than ASIC-based bitcoin cryptocurrency mining.
- There is no need for dedicated hardware or frequent hard disc upgrades.
- The mining data can be simply erased, and the drive can be repurposed for other data storage needs.
Cons
- The technology has been embraced by a small number of developers.
- Malware has the potential to disrupt mining operations.
- Widespread adoption of PoC could spark a "arms race" to create larger hard drives.
What is Chia (XCH)?
If you're reading this, it's probable that you've previously heard about Chia and are merely interested in learning how to mine it. If that's the case, move on to the following section. If not, we've got a quick rundown of the new cryptocurrency for you:
Chia is a relatively new cryptocurrency, being launched in March of this year. It was created to be a more energy-efficient crypto by Bram Cohen, who also built BitTorrent. Rather than standard GPU mining, which is utilised by more mainstream cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, it uses the power of storage devices to farm crypto.
Chia's popularity has exploded in recent weeks, causing hard drive and SSD shortages in China that could soon be replicated in the United States and elsewhere.
With cryptocurrencies like Dogecoin seeing large hype-fueled price spikes despite having no fundamental worth (Dogecoin has no coin cap and can expand indefinitely), it appears like Chia's price will rise as its popularity grows. It has a total coin cap of 21 million, which is the same as Bitcoin.
Chia use a unique method known as "Proof of Space and Time," or PoST, which essentially verifies that you have free space on your hard drive or SSD that can be utilised for farming. It outperforms Bitcoin's Proof of Work algorithm in terms of efficiency.
Can I buy or sell Chia?
Because chia trades are now unavailable, the only way to obtain the currency is by farming. This functionality should be available on May 3rd around 10 a.m. Pacific Time, according to Chia's official website (1PM Eastern Daylight Time).
What do I need to mine Chia?
To mine Chia, you'll need at least some free storage space; the more, the better. You'll also need to meet Chia Blockchain's minimal system requirements, which are as follows:
- Quad-core 1.5GHz CPU
- 2 GB of RAM
- Python 3.7 or above
These needs should be readily met by any modern computer, thus the only limiting element for you will most likely be storage capacity.
Which is more important, storage space or drive speed?
If you want to maximise your Chia farming efficiency, you'll need both read/write speed and total storage capacity. You should have at least one fast drive (ideally with a large capacity) for temporary storage and one larger-capacity hard drive for storing your completed plots.
How can I join a Chia mining pool?
Pooling functionality is currently unavailable in Chia. Pooling is the process of pooling hashing power (or, in this case, hard drive space) with other miners to increase your chances of winning a cryptocurrency.
If your mining pool accounts for 50% of the network's overall farming capacity, you'll receive roughly half of the Chia, which is then shared among pool members based on how much they contributed. Pooling, in essence, removes the element of chance from farming.
As a result, Chia does not currently support this feature. Unless you have a very large storage farm, your ability to generate Chia will be primarily dependent on luck. However, because the prize will not be split, the upside will be greater.
Pooling, on the other hand, will be added (as per Chia's blog), and we'll update this once that feature is enabled.
How to mine Chia: Step-by-step guide
Let's get to the fun part: farming, now that we've covered the basics of Chia. It is incredibly simple to set up a computer for Chia cultivation.
Install Chia Blockchain:
Chia Blockchain, Chia's proprietary farming client, is available for download here. The download will begin after you select the proper option for your operating system. Run the ChiaSetup-X.X.X.exe file after it has been downloaded to go to this page:
 |
| Chia’s sign-in page |
Create your wallet:
It's now time to make your wallet, which will house all of the Chia you'll ever farm. When you choose Create A New Private Key, you'll be presented with a screen having 24 words on it. Because these words are used to access your wallet, be sure to write them down (in order) or snap a picture of them and save it somewhere safe. And, of course, don't tell anyone about your word list.
 |
| A example of a Chia word list |
When you click next, Windows Firewall or your OS's security application may prompt you to grant Chia access to specific rights. "Allow" should be selected.
Create a plot
You're ready to start farming now that you've downloaded Chia Blockchain and created a wallet. To do so, go to the side of the screen and select the "Plots" tab. You'll be taken to a screen that looks like this:
 |
| Chia Blockchain’s Plots interface |
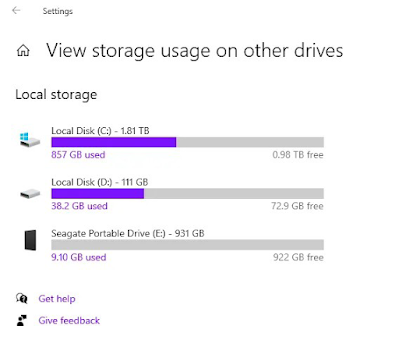
To begin, determine how much storage space you have available. In the Windows search box, type Storage Settings, scroll down, and click View Storage Usage on Other Drives. Non-Windows operating systems have a similar feature; go to your operating system's storage options to check how much space you have available.
 |
| Windows 10 Storage Usage |
I have almost 900GB accessible on both my E and C drives in the example above. I'll create a plot on each of these discs because I don't need this storage right now and won't in the near future.
In other words, figure out how much storage you have and how much of that unallocated storage you're willing to use. Use this information to help you decide on a plot size, which we'll discuss in a moment.
Select Add a Plot when you return to the Chia Blockchain software.
 |
| Chia Blockchain’s Add a Plot interface |
The options shown above will be presented to you. You can choose the number of plots, plot size, and the temporary and final directories where your plot (a literal.PLOT file) is saved.
You can opt to plot in parallel or add a plot to the queue when you select plot count. If you have enough storage, you can plot in parallel or make two plots on the same storage device at the same time.
If not, you can queue up to 29 plots at a time to ensure that your storage continues to farm even when you aren't using it.
It's best to utilise a speedier disc for temporary storage (preferably an NVMe SSD for optimal speeds) and a large-capacity hard drive for permanent storage.
You may also change advanced options like the maximum RAM and CPU thread use. Feel free to allocate more than the default amount for your plot if you have extra RAM or threads. Farming speed will increase slightly as a result of this.
It's worth noting that the "threads" option refers to "threads per plot" rather than "total threads." As a general guideline, we recommend using two plots per plot to allow you to produce the most plots in parallel at the fastest possible speed.
If you're not sure how much RAM you have, launch Task Manager by pressing ctrl + shift + esc, then go to the Performance tab and check your memory. It will display how many GB of RAM is currently in use, allowing you to quickly calculate how much is still available.
Finally, you should leave the number of buckets set to the default value of 128. You can also modify the queue name if you like; it will have no effect.
Click Create Plot once you've optimised the options for your machine. Your farm is now accessible to the public!
 |
| Advanced plotting options |
What are MiB and GiB?
You'll notice that Chia Blockchain's five plot size presets measure storage in MiB and GiB rather than the more common MB and GB when you go to choose your plot size. So, what's the difference?
 |
| There are currently five preset plot sizes available |
The quick answer is that they're essentially the same; the only difference is that MiB (Mebibytes) and GiB (Gibibytes) are based on powers of two rather than ten. As a result, a mebibyte is 1,048,576 bytes, a megabyte is one million bytes, and a gibibyte is around 1.07 gigabytes.
When measured in GB and MB, figures expressed in GiB and MiB are slightly greater. To figure out which preset is ideal for you, you can utilise a conversion calculator.
Wait for your farms to produce
All that's left to do now is sit and wait after your farm is up and running. If your system has enough resources, you can add more plots, but otherwise it's a waiting game.
When your plots are finished, they should start farming on their own. When you see a screen like the one below in the farming GUI, you'll know.
The Plots interface allows you to see your plots and their development. Your plot will be relocated to its final storage disc after it is finished. You'll get 2 Chia if one of the values in your plot is closest to the "challenge value" broadcast on Chia's blockchain. Every 10 minutes, a new challenge value is revealed.
The more plots worth of storage capacity you have, the more likely you are to plot the winning number.
 |
| We hope you found this guide useful. As more features, including as transactions, become available, we'll expand our coverage of Chia. Best wishes and happy farming! |